

- Aashto 1993 pavement design guide pdf manual#
- Aashto 1993 pavement design guide pdf verification#
- Aashto 1993 pavement design guide pdf software#
- Aashto 1993 pavement design guide pdf plus#
Aashto 1993 pavement design guide pdf verification#
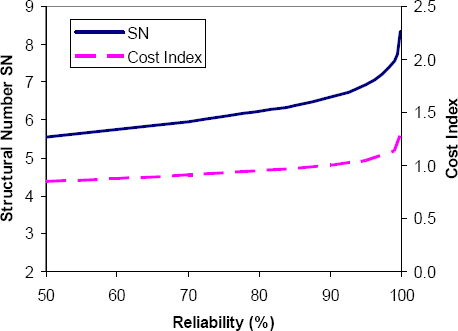
It was recommended that the calibration and verification of the AASHTO-Ontario model should be a continuous process and that the quality and quantity of the database should be improved to serve the needs of the 2002 Guide. Results of calibration and verification processes indicate that for new flexible pavements, the AASHTO-Ontario model is in good agreement with the observed results. The end result was a new grouping of Ontario soils for pavement design, recommended values for the resilient modulus of below grade soils, recommendations for structural layer coefficients for Ontario pavement materials and recommendations for the initial pavement serviceability based on Ontario smoothness specifications. Otherĭata was also collected from research and development studies, laboratory experiments, and from a survey of experienced pavement design engineers. Data collected on Ontario highway pavements and materials was used for assessing the design inputs. The AASHTO Guide uses two parameters to deal with design reliability: design reliability level and overall standard deviation.
Aashto 1993 pavement design guide pdf plus#
The paper focused only on the design of flexible pavements in terms of load characterization using equivalent single axle loads along with axle load spectra, below grade and material characterization, plus initial and terminal serviceability and reliability. A summary was also provided of the additional work done to prepare for the transition to the proposed mechanistically-based 2002 AASHTO Guide. The factors are summarized to yield the number of Equivalent Single Axle Loads (ESALs) a pavement is expected to sustain during its life. The size of LEF is related to the damage that is expected to occur from a standard load of 80 kN carried by a single axle with dual tires. LEF is regarded as a pavement damage factor assigned to each specific load and axle configuration. The guide expresses the effect of traffic loads on pavement performance using the concept of axle Load Equivalency Factors (LEF).
Aashto 1993 pavement design guide pdf manual#
Software: NJ Companion Manual to AASHTO 1993 Design Guide (swf 1.The methodology used to adapt the 1993 AASHTO Guide for Design of Pavement Structures to Ontario conditions was described.

Aashto 1993 pavement design guide pdf software#
Please contact the Pavement design Unit for most updated information of design policy and/or current Specifications for a specific project.ĭownload the following presentations: Software Demonstration (swf 373k) Training and/or Presentations may have been updated and/or modified or may have been obsolete. The Presentations and/or Trainings presented here have been prepared based on the practices and methodologies that were current at the time of preparation. Design decisions are not to be made solely on the presentations and/or training. The presentations and/or training are provided for reference purpose and may not be applicable in the fullest extent to specific projects.
Pavement rehabilitation is needed for deficient roadways, but pavement preservation can extend pavement life for state highways in good and fair condition. NJDOT's Pavement and Drainage Management and Technology Unit is advancing the use of Pavement Preservation treatments on the state's roads to increase safety, enhance durability, improve customer experience and minimize costs. To assist in the cost effective and efficient design and construction of roadway pavements, NJDOT presents the following guidance, presentations, web links and examples:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
